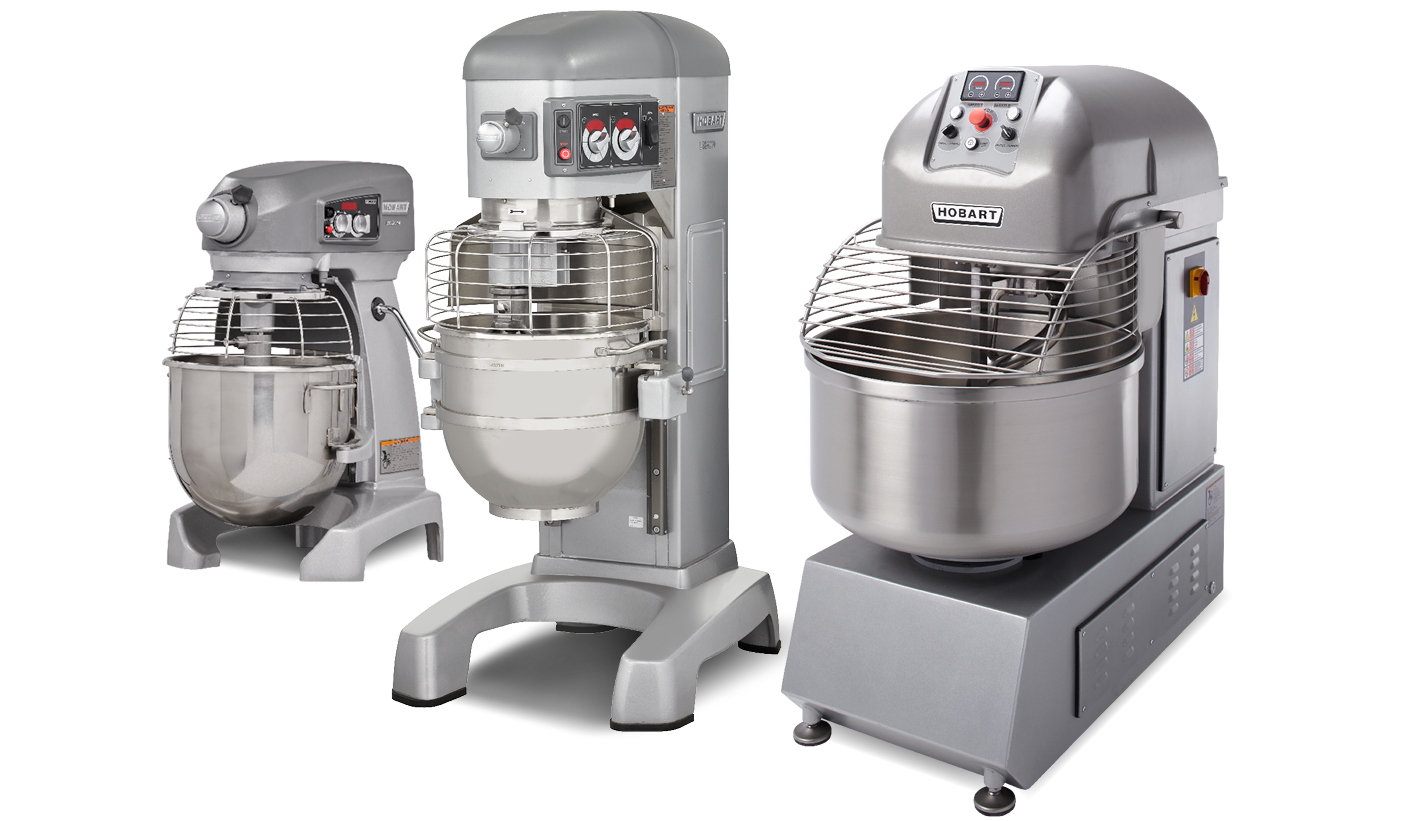
Misconception 1: Larger motor = more power
When it comes to mixers, looking at just the advertised horsepower doesn’t provide a complete picture of the performance that can be expected. A larger motor doesn’t necessarily mean the mixer provides more power. Instead, it’s important to consider the mixer’s efficiency and torque, which affect the equipment’s ability to drive the agitator into the bowl to incorporate product thoroughly. The type of drive system the mixer has is a key factor. For example, Hobart® Legacy+ mixers with Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) use a variable -speed motor and a single gear train that regulates the frequency and voltage of the electrical current to the motor. VFD controls the mixer’s speed, increasing and decreasing it as required to put the right amount of torque into the bowl for consistent mixing. If a mixer requires a larger motor to drive the same amount of torque as a smaller motor, it is likely expending too much energy for the job. This can lead to premature failure of the motor due to components becoming hotter faster — and increase costs for repairs or replacement.
Misconception 2: More is always better
Considering the application for the mixer is key to determining the size and type of mixer to buy. First, it’s important to have the right size of bowl to achieve thorough mixing and avoid taxing the motor. In some cases, a larger-volume bowl will be necessary, but not always. It is a matter of absorption ratio (AR). The AR calculation is water weight divided by flour weight. This is an important factor, since the recommended maximum capacity of the mixer depends on the moisture content of the dough. On the Hobart mixer capacity chart, the capacities are based on an absorption rate calculation formula of 12% flour moisture at 70-degree Fahrenheit water temperature. Also, not all kitchens require a maximum heavy-duty mixer. If the mixer will be used to periodically mix heavy doughs or for limited-batch use, a standard heavy-duty mixer, like the Centerline™ by Hobart HMM20 may be the better choice. The Centerline mixer is intended to mix for less than four hours daily and is a good option for kitchens seeking a reliable, cost-effective mixer for multiple applications.
Misconception 3: Routine maintenance isn’t critical
While mixers aren’t as complicated as some other kitchen equipment, that doesn’t mean that routine preventive maintenance isn’t important. Mixers have lubrication points that need attention, such as the actuators that assist in lifting and lowering the bowl. Follow the manufacturer’s recommended amount and frequency for greasing these points. Take care not to wipe off all of the grease off during cleaning. Doing so can prevent the bowl from moving up and down properly. Regularly monitor the bowl clearance for consistency. If the agitator is hitting the bottom of the bowl, it can lead to wear and possible damage. Conversely, if the agitator is too far from the bowl, ingredients won’t be mixed fully. The operator’s manual can often provide adjustment instructions, as can a service provider. Consider having a service provider visit once or twice annually to inspect the mixer. A proactive approach to maintaining the equipment can help reduce costs in the long term.
About the Author
.jpg?width=67&height=67&name=Bilger%20Carolyn%201%201x1-2_%20(002).jpg) Carolyn Bilger is the marketing director for Hobart – Food Preparation Products. She has been with Hobart since 2015 and sets the strategy for marketing and new product development for the full line of Hobart food preparation equipment. See all her blogs here.
Carolyn Bilger is the marketing director for Hobart – Food Preparation Products. She has been with Hobart since 2015 and sets the strategy for marketing and new product development for the full line of Hobart food preparation equipment. See all her blogs here.




-min.jpg)